Cell
Cell- The smallest unit that can live on its own and that makes up all living organisms and the tissues of the body:
Robert Hooke (1635-1703) in 1665 made thin section of wood cork and observed them under a microscope. He found there numerous little boxes like bee hives. Then he remembered seeing such small rooms for the priests to stay in the monastery. From this, he named the cork’s little box as “cell”. The word cell is derived from the Latin word cellula, means little box.
Pic: Cell, Photo Credit: freepik.Table of Contents
Deffinition
Different scientist defined cell with different definitions. Some of them noted below- According to Jean Bracket (1961), ‘Cell is the basic structural unit of an organism.’
- According to Loewy and Siekevitz (1963), a cell is a unit of biological activity surrounded by a semi permeable membrane and capable of self reproduction without any help of other living medium.
- According to C. P Hickman (1970), Cell is the unit of biological structure and function and is the smallest biological unit capable of self-regulation and reproduction.
- According to De Roberties (1979), a cell is the basic structural and functional unit of an organism.
Characteristics
- Cells carry all the structural and molecular components necessary for life.
- Necessary raw materials can be taken inside.
- It can collect the necessary energy by using raw materials and synthesize its own necessary molecules.
- Can grow in a controlled manner.
- Can respond to any surrounding stimuli.
- Can maintain a homeostatic state (i.e. an internal steady state despite changes in environmental conditions).
- Can be evaluated during course of time.
Types
Based on physiological activity:- Somatic Cell:
Cells that build the organs and organ systems of living organisms are called somatic cells. Somatic cells of higher organisms usually have diploid number (2n) of chromosomes. For example: Cells in roots, stems, leaves, nerves and blood vessels. - Reproductive Cell or Gamete:
The haploid cells produced by the process of meiosis in the genitalia of diploid organisms for sexsual reproduction are called gamete cells. Sperm and egg are the example of gametes. Gametes are always haploid (n) in number.
Name two types of cells in the basis of nature of nucleus:
- Prokaryotic:
that do not have a true and organized nucleus, cell membranes and chromosomes, are called prokaryotic cells .Example included Bacteria, blue green algae etc. - Eukaryotic:
that have a well-organized or organized nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles are called eukaryotic cells. That is, the cells in which the nucleus is organized (nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, nucleolus and nuclear reticulum are present) and nuclear membrane is surrounded, chromosomes contain alkaline protein, cell membranes are surrounded by multiple cell organelle, called eukaryotic cells. For example: plant and animal cells.
Structure
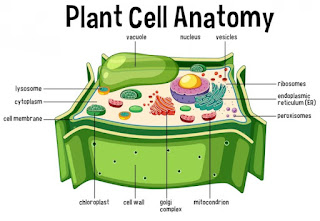
A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell that forms the basic structural unit of a plant. It has a complex structure with various membrane-bound organelles that carry out specific functions. The main components of a typical plant cell are:
Pic: Plant Cell, Photo Credit: freepik.


Comments
Post a Comment